Vespa Newsletter, February 2026
Welcome to the latest edition of the Vespa newsletter. In the previous update, we introduced several new features and improvements, including Automated ANN Tuning, Accelerated Exact Vector Distance with Google Highway, Precise Chunk-Level Matching for Higher Retrieval Quality, Quantile Computation in Grouping for Instant Distribution Insights, and more.
This month, we’re announcing several updates focused on retrieval quality, ranking flexibility, and developer productivity. Each feature is designed to help engineering teams build faster, more accurate, and more maintainable retrieval and ranking systems, while giving businesses better relevance, lower operational overhead, and more predictable performance at scale.
Let’s dive into what’s new.
Product updates
- Announcing the Vespa.ai Playground
- The Vespa Kubernetes Operator
- Faster result rendering with CBOR
- Pyvespa 1.0 with improved HTTP performance
- Hybrid search relevance evaluation tool
- Configurable linguistics per field
- “switch” operator in ranking expressions
- Vespa is now available on GCP Marketplace
- Feed data and run queries in the Vespa Console
Announcing the Vespa.ai Playground
The Vespa Playground is a new GitHub space where we share projects, tools, and demos built on the Vespa platform. It’s a practical place to explore real examples for embeddings, model training, and feed connectors that you can clone, run, and build on your own.
These repos are ideal for experimentation, learning, and inspiration, though they aren’t officially supported product releases.
The Vespa Kubernetes Operator
The safest, most robust and cost effective way to run Vespa is to deploy on Vespa Cloud, but for various reasons that’s not an option for everybody. For those who want to run Vespa securely at scale but can’t use Vespa Cloud we have now released the Vespa Kubernetes Operator. This brings many of the Vespa Cloud features such as security out of the box, dynamic provisioning, autoscaling and automated upgrades to your own Kubernetes environments.
Read more in the Kubernetes Operator documentation.
Faster result rendering with CBOR
Query result sets can be large, and increasingly so when the client is an LLM retrieving many chunks for model context. Layered ranking is designed to address this by extracting the most relevant content. Still, in some cases, the total latency is dominated by the time it takes to send the query response. Compressing with gzip can help, but is also CPU-intensive and slow.. From Vespa 8.623.5, json response generation is over twice as fast as before.
Another new option in this release is to use the CBOR format for query results. CBOR is a binary format so it can be serialized faster and produces smaller payloads, especially when the result contains lots of numeric data. Read more in the Query API reference and query performance guide.
Pyvespa 1.0 with improved HTTP performance
We have released the first major version of Pyvespa! This release switches the HTTP-client used by Pyvespa, from httpx to httpr, which gives big performance gains, especially for serializing and deserializing tensors, largely by taking advantage of the new CBOR serialization support in Vespa.
On preliminary benchmarks, we compared end-to-end latency for:
-
Vespa 8.591.16 + Pyvespa v0.63.0 (using JSON)
-
Vespa 8.634.24 + Pyvespa v1.0.0 (using CBOR)
The latter was ~4.9x faster when returning 400 hits with a 768-dim vector each. Performance gains will be smaller when not returning large result sets with tensors, but still significant. You may encounter different exceptions than before, but we strived to not change any user-facing API’s even if we bumped the major version.
Hybrid search relevance evaluation tool
Hybrid search combines lexical and embedding based search to get the best from both. One of the tasks you need to solve is to pick an embedding model that provides a good quality vs. cost tradeoff for your use case. We have done a systematic evaluation of modern alternatives in this blog.
The code used to run these experiments is now merged into Pyvespa. You can use the VespaMTEBApp to evaluate embedding model performance on any task/benchmark compatible with the mteb-library. See example usage from the tests.
Configurable linguistics per field
Vespa now lets you specify linguistics profiles on fields to select some specific linguistics processing in your Linguistics module. In Lucene Linguistics, linguistics profiles map to analyzer configuration, optionally in combination with a specific language.
For example, you can define a Lucene analyzer like this in services.xml:
<item key="profile=whitespaceLowercase;language=en">
<tokenizer>
<name>whitespace</name>
</tokenizer>
<tokenFilters>
<item>
<name>lowercase</name>
</item>
</tokenFilters>
</item>
And use it in the schema, under any field’s definition, like this:
field title type string {
indexing: summary | index
linguistics {
profile: whitespaceLowercase
}
}
By default the linguistics profile will be applied both when processing the text of the field and the text searching it, but you can also specify a different linguistics profile on the query side, which is useful for e.g. doing synonym query expansion.
We’ve added a sample application demonstrating how to use multiple Lucene linguistics profiles across multiple fields and updated the Vespa linguistics documentation with usage examples.
New “switch” operator in ranking expressions
We have added a “switch” function in ranking expressions as a clearer, more maintainable alternative to deeply nested if() clauses, making complex ranking easier to read, debug, and evolve.
switch (attribute(category)) {
case "restaurant": myRestaurantFunction(),
case "hotel": myHotelFunction(),
default: myDefaultFunction()
}
Vespa is now available on GCP Marketplace
Vespa Cloud is now listed on the GCP Marketplace, making it easier to deploy and manage Vespa using native Google Cloud billing and procurement. Vespa Cloud is already available on AWS Marketplace.
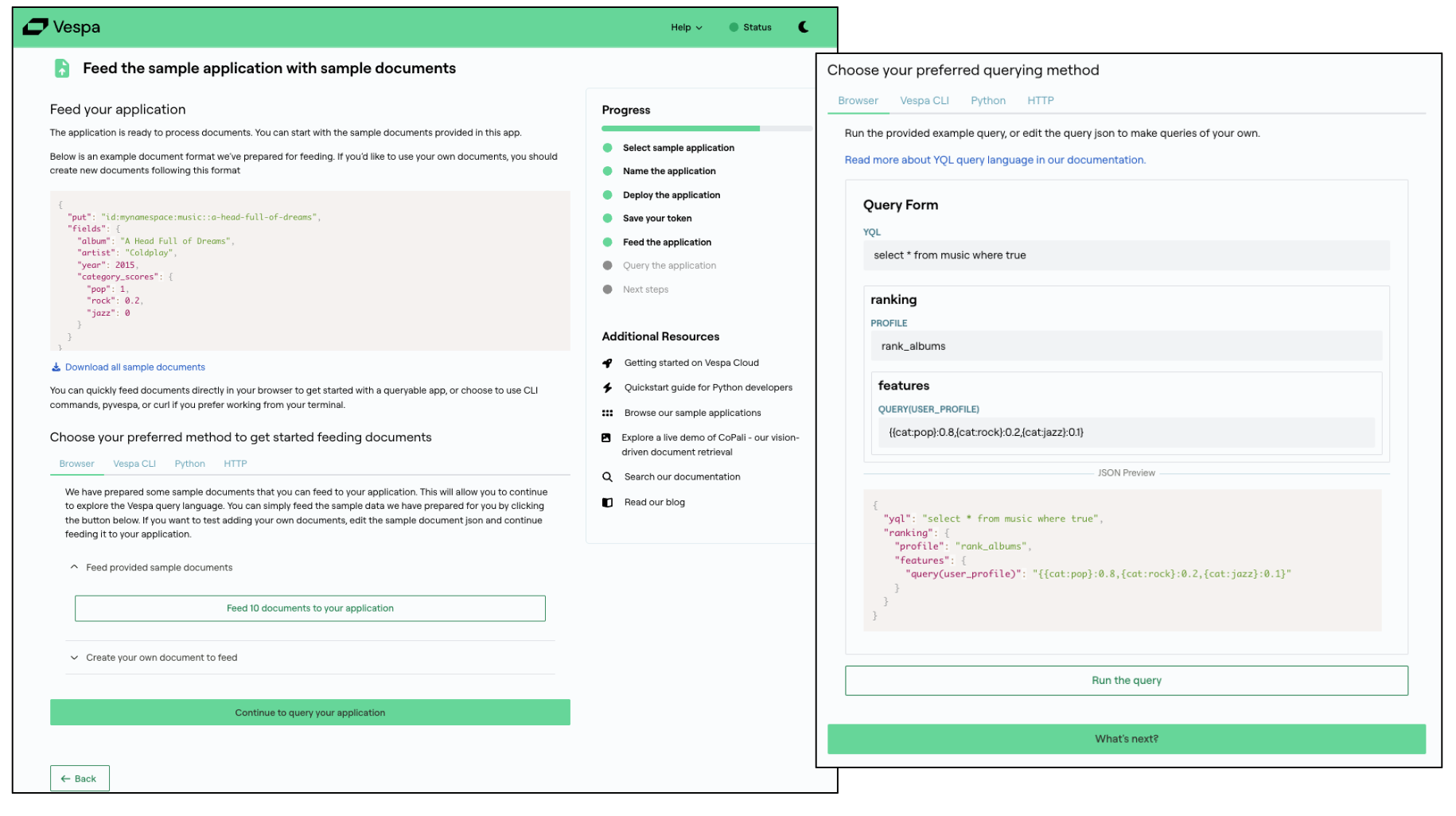
Feed data and run queries in the Vespa Console
The onboarding experience is now even smoother for new Vespa Cloud users. When you follow the getting started guide and deploy a sample app from the browser, you can immediately feed data and run queries directly in the browser. This makes it easy to try your own data and see how it behaves in Vespa.
We also provide examples showing how to do the same using pyvespa, the Vespa CLI, or curl.
New content and learning resources
We published several new articles and resources since our last newsletter to help teams get more out of Vespa and stay ahead of new developments in search, RAG, and large-scale AI.
Examples and notebooks:
Videos, webinars, and podcasts
Blogs and ebooks
- Clarm: Agentic AI-powered Sales for Developers with Vespa Cloud
- Embedding Tradeoffs, Quantified
- Enterprise AI Search vs. the Real Needs of Customer-Facing Apps
- Eliminating the Precision–Latency Trade-Off in Large-Scale RAG
- How Tensors Are Changing Search in Life Sciences
- The Search API Reset: Incumbents Retreat, Innovators Step Up
- Why AI Search Platforms Are Gaining Attention
- Why Life Sciences AI Is a Search Problem (Part 5 of 5)
- Why Life Sciences AI Is a Search Problem (Part 4 of 5)
Upcoming Events
 Lightning Lesson: Personalized Relevance with VLMs and Sparse Vectors: February 17, 11:30am ET
Lightning Lesson: Personalized Relevance with VLMs and Sparse Vectors: February 17, 11:30am ET
- Intro to sparse vectors and tensors for efficient data handling
- Using Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to extract high quality and nuanced features from images
- Leveraging these features in sparse representations for hyper-personalized search & recommendations
 February 18: The Zero Results Problem in eCommerce
February 18: The Zero Results Problem in eCommerce
- 🔗 10am CET (EMEA): Save your spot
- 🔗 1pm ET (Americas): Save your spot
March 11: The Relevance Problem in eCommerce
- 🔗 10am CET (EMEA): Save your spot
- 🔗 1pm ET (Americas): Save your spot
 March 10: Vespa Q1 Product Update
March 10: Vespa Q1 Product Update
- 🔗 10am CET (EMEA): Save your spot
- 🔗 1pm ET (Americas): Save your spot
👉 Follow us on LinkedIn to stay in the loop on upcoming events, blog posts, and announcements.
Thanks for joining us in exploring the frontiers of AI with Vespa. Ready to take your projects to the next level? Deploy your application for free on Vespa Cloud today.