The big data maturity levels
By now it’s well known that making effective use of data is a competitive advantage. But how advanced is your organization at making use of data?
Over the last few years I have spoken to many organizations on this topic. One thing I’ve learned is that all of them go through the same learning process in putting their data to work. From Silicon Valley giants to industry companies in Asia and government entities in Europe, all go through the same main evolutionary stages. I call these the big data maturity levels.
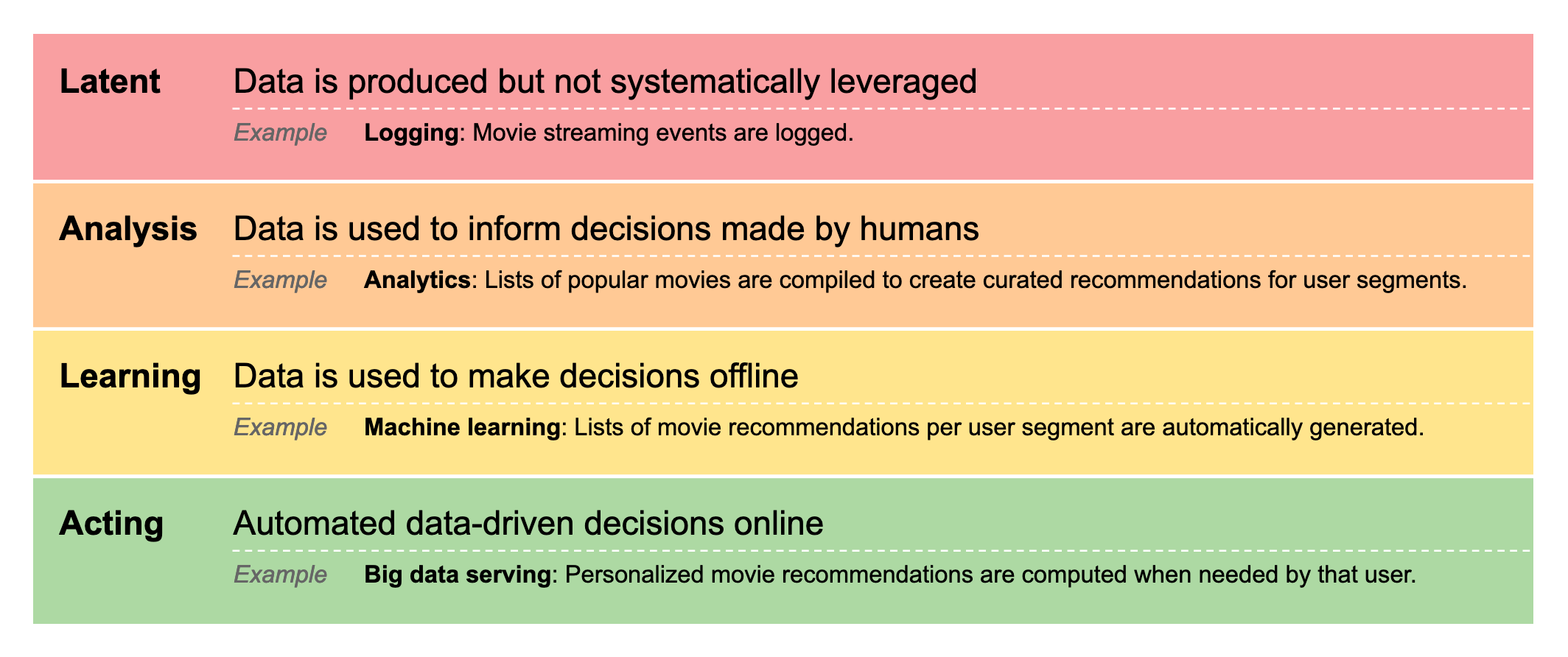
Level 0: Latent
Data is produced by the normal course of operations of the organization, but is not systematically used to make decisions.
Example: A movie streaming service is logging each movie viewing event with information about what is viewed, and by whom.
Level 1: Analysis
Data is used by humans to make decisions. Analysts extract information from the data, such as graphs and figures showing statistics, which is used by humans to inform their decision making.
Example: A movie streaming service uses logs to produce lists of the most viewed movies broken down by user attributes. Editors use these to create curated movie recommendations to important segments of users.
Relevant technologies at this level include traditional data warehouses, data analytics platforms such as Splunk and Elastic Search, and big data query engines such as Spark.
Level 2: Learning
Data is used to learn and compute the decisions that will be needed to achieve a given objective. Rather than making each decision directly from the data, humans take a step back from the details of the data and instead formulate objectives and set up a situation where the system can learn the decisions that achieve them directly from the data. The offline system both learn which decisions to make and computes the right decisions for use in the future.
Example: A movie streaming service uses machine learning to periodically compute lists of movie recommendations for each user segment.
Relevant technologies at this level include machine learning tools such as TensorFlow and PyTorch, machine learning platforms such as Michelangelo, and tooling for offline processing and machine learning at scale such as Hadoop.
Level 3: Acting
Data is used to make decisions in real time. Rather than pre-computing decisions offline, decisions are made at the moment they are needed. This makes it possible to take all relevant information into account and base decisions on up-to-date information about the world.
Example: A movie streaming service computes recommended movies for each particular user at the point when they access the service.
Relevant technologies: Some times it is possible to make decisions by considering a single data point. In those cases model serving tools such as TensorFlow Serving, or stream processing tools such as Storm and Flink may be used. In general — as in the movie streaming example - multiple data items are needed to make each decision, which can is achieved using a big data serving engine such as Vespa.
Conclusion
Taking a step back and reflecting on the maturity level of your organization (or team — organizations don’t always evolve in synchronicity) can be helpful in understanding the current type of challenges you face, what kinds of technologies you should consider, and what’s needed to move to the next level in your organization.
I hope this post has been helpful in this — it’s the first post in a series exploring this topic. In the next posts, I’ll take a look at the forces that pushes the worlds most advanced organizations to move to maturity level 3, the benefits they see from making this move, and why this has traditionally been so hard to pull off.